lm(RFFT ~ Age, data = prevend.samp)
Call:
lm(formula = RFFT ~ Age, data = prevend.samp)
Coefficients:
(Intercept) Age
137.550 -1.261 Class 26
Two numerical variables
What kind of association is there between them?
Lots of possibilities
First resource: scatterplot!
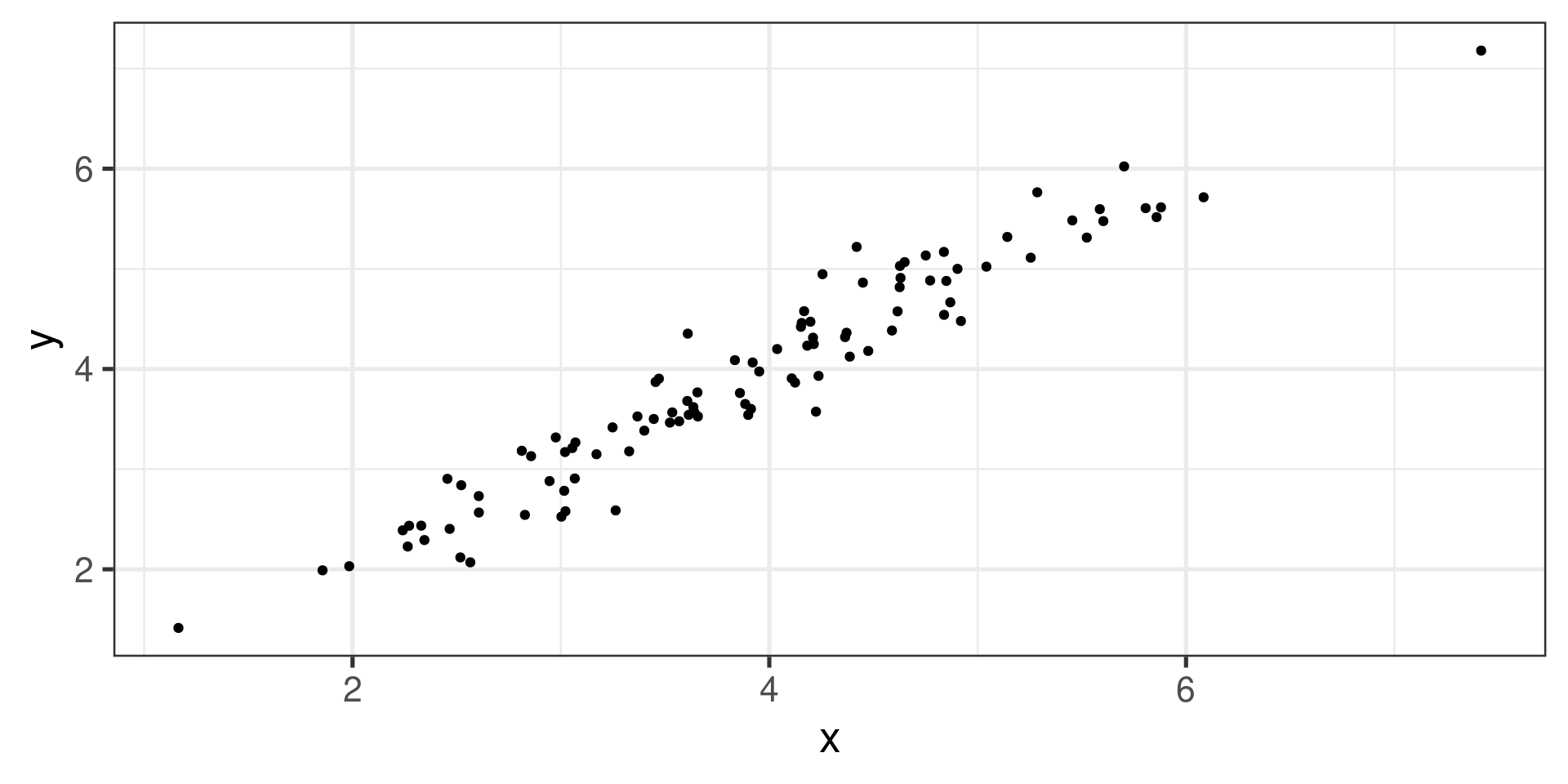
Positive linear association
Positive linear association, much weaker
Strong negative linear association
Non-linear association
Non-linear association
Unclear (very weak linear) association
No association, or very weak association
Not applicable if the scatterplot shows a nonlinear association!
Use only if scatterplot shows a linear association or no clear association
Start by moving data so that the point
Multiply together and calculate the mean
To compensate for different spreads, divide by both standard deviations
where:
In R: cor(x,y) or cor(y ~ x, data = ...)
Between
if
Population correlation coefficient is denoted
We have a sample with correlation coefficient
Permutation test!
We can also calculate a t-statistic:
This has t-distribution with
What now?
Find a mathematical model for the association:
Data is scattered, so the relation will actually be
Official name for the “noise” is residuals.
predicted value of
actual or observed value of
The population model:
The estimate based on the sample:
The population model:
The estimate based on the sample:
and
Usually done by computer
lm(RFFT ~ Age, data = prevend.samp)
Call:
lm(formula = RFFT ~ Age, data = prevend.samp)
Coefficients:
(Intercept) Age
137.550 -1.261 The least squares line can be written as